Embark on a journey to uncover the mysteries of the Salton Sea, a unique and evocative body of water shrouded in intrigue and history. Nestled in a location that might surprise you, this enigmatic sea holds tales of nature’s power and human ambition. Discover what makes the Salton Sea a topic of fascination and controversy. Join us as we explore its geographical whereabouts, revealing the secrets that lie within its waters and beyond.
Geographic Location of Salton Sea
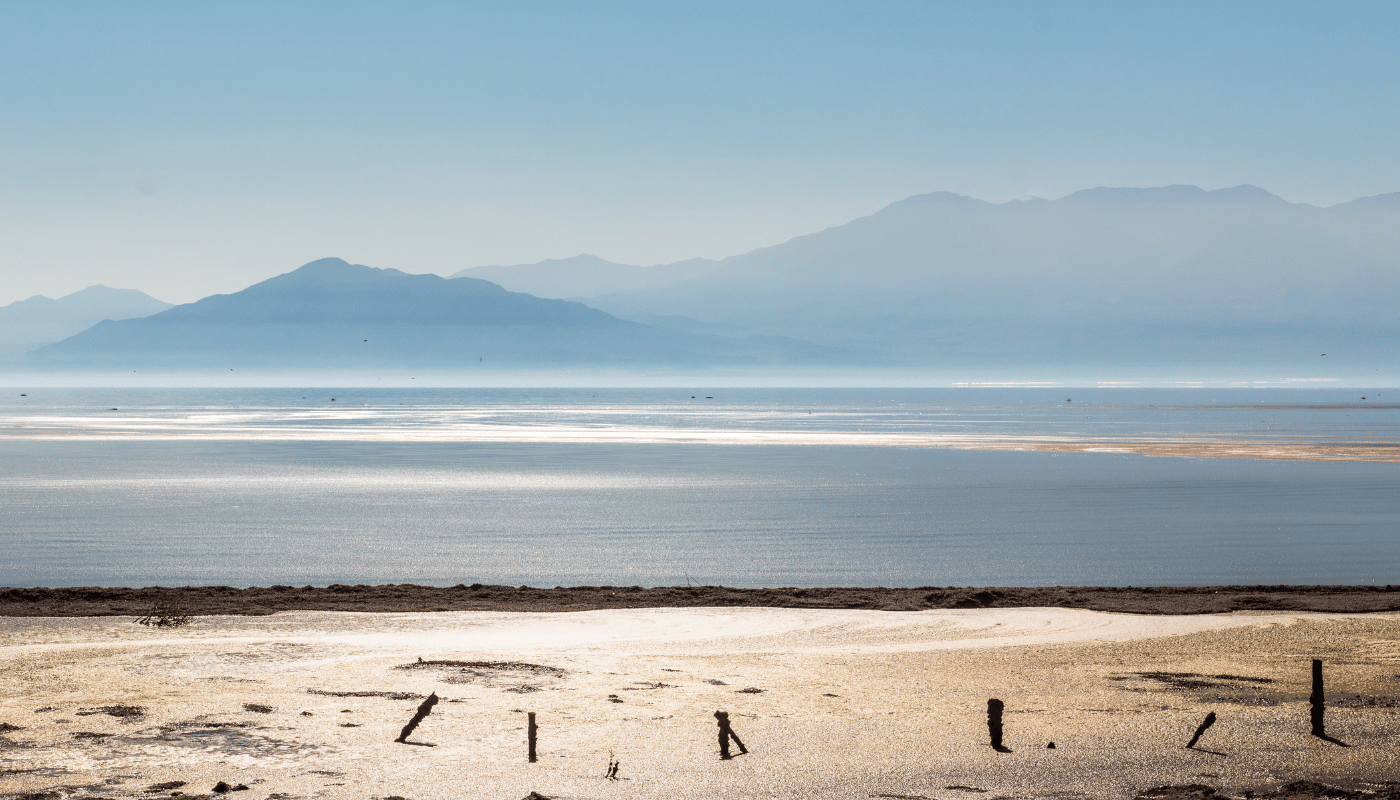
The Salton Sea, often questioned as ‘where is the Salton Sea?’, is an intriguing geographical anomaly located in the southeastern part of California, United States. Nestled in the Coachella Valley, this saline lake lies directly on the San Andreas Fault, which significantly influences its geological and ecological characteristics. The Salton Sea occupies the lowest elevations of the Salton Basin, a part of the larger Colorado Desert.
Historically, the Salton Sea was created in 1905 when the Colorado River, swollen with heavy rains and snowmelt, breached its levees and flooded into the Salton Sink. Over the course of approximately two years, the basin was filled, creating the largest lake in California by surface area. Today, it is bordered by the cities of Indio, Coachella, and Brawley, and it serves as a critical habitat for various species of birds and fish, despite its increasing salinity and environmental challenges.
The significance of the Salton Sea is not just limited to its unique formation and location. It plays a crucial role in the migratory patterns of many bird species and acts as an essential stopover on the Pacific Flyway. However, the Salton Sea is facing pressing environmental issues, such as rising salinity and decreasing water levels, which threaten its ecosystems and the surrounding communities. Efforts are ongoing to mitigate these challenges and preserve the Salton Sea for future generations.
- Located in southeastern California, within the Coachella Valley.
- Occupies the Salton Basin, part of the Colorado Desert.
- Created by flooding from the Colorado River in 1905.
- Largest lake in California by surface area.
- Important habitat for migratory birds and endangered species.
The Enigmatic Presence of the Salton Sea
Located in California’s Imperial and Coachella valleys, the Salton Sea is the largest lake in the state, a result of a flooding accident in 1905. What was once a thriving tourist destination in the 1950s and 60s, attracting visitors with its promise of resort luxury and abundant wildlife, has now become an eerie, almost post-apocalyptic landscape. The salinity of the water is higher than that of the Pacific Ocean, making it inhospitable for most fish and bird species that once thrived here.
Despite its current state, the Salton Sea holds significant importance in terms of ecology and potential renewable energy resources. Its location is pivotal, sitting atop the San Andreas Fault, lending to geothermal activity below its surface. This has piqued the interest of scientists and investors alike, looking towards geothermal energy as a clean, sustainable resource. However, the area is also a stark reminder of human impact on natural habitats, with the lake’s shrinkage exposing toxic dust that poses health risks to nearby communities.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in the Salton Sea, not just from environmentalists keen on its preservation but also from artists and photographers drawn to its desolate beauty. The stark contrast between its past allure and its present condition serves as a powerful narrative on transformation and resilience, making the Salton Sea a subject of fascination and study across various disciplines.
Additional Insights into the Salton Sea’s Complex Ecology
The ecological dynamics of the Salton Sea are both fascinating and troubling. As water levels have declined, salinity has increased, leading to the collapse of fish populations that birds relied on for food. This has caused a dramatic decrease in bird populations, affecting the Pacific Flyway, a major north-south flyway for migratory birds in America. Efforts are underway to mitigate these impacts, including habitat restoration and water quality improvement projects. Understanding the delicate balance of this ecosystem is crucial for any conservation strategy to be successful.
Further Perspective on the Salton Sea’s Geothermal Potential
The underexplored geothermal resources beneath the Salton Sea represent a significant opportunity for renewable energy development. With one of the highest geothermal potentials in the United States, the area could contribute substantially to California’s energy needs if harnessed properly. This not only offers a path towards sustainable energy but also provides a chance to redefine the Salton Sea’s role in the region’s economy and environmental health.
- The history and creation of the Salton Sea.
- Impact of salinity levels on wildlife and habitat.
- Human and environmental health risks associated with the lake’s decline.
- The role of the Salton Sea in geothermal energy potential.
- Conservation efforts and future prospects for the area.
Historical Significance of the Salton Sea
The Salton Sea, a vast saline lake located in California’s Imperial and Coachella valleys, holds a rich tapestry of history that is as varied as it is fascinating. Formed in 1905 due to a breach in irrigation canals from the Colorado River, it became a testament to human engineering both failing and adapting to the whims of nature. Initially, the area was envisioned as an agricultural haven, but the accidental creation of the sea changed the region’s trajectory, turning it into a booming resort area in the 1950s and 60s. Celebrities and families alike were drawn to its shores, mesmerized by the promise of recreation and beauty.
However, the Salton Sea’s story is also one of ecological caution. As agricultural runoff increased, the sea’s salinity began to rise, and by the late 20th century, environmental concerns overshadowed its once-glamorous appeal. Fish die-offs and pollution issues became synonymous with the area, turning it into a stark example of environmental degradation. Yet, its historical significance extends beyond these challenges. The Salton Sea has served as a crucial habitat for migratory birds, playing a vital role in the Pacific Flyway. Despite its problems, it remains an important site for biodiversity, research, and education on the impacts of human actions on natural landscapes.
Today, the Salton Sea stands as a poignant reminder of the balance between development and nature conservation. It is a subject of scientific study and restoration efforts, aiming to preserve its unique ecosystem while acknowledging its complex history. The Salton Sea’s story is a compelling chapter in California’s environmental and cultural narrative, embodying themes of transformation, resilience, and the ongoing quest for sustainability.
- Formation in 1905 due to irrigation canal breach
- Boom as a resort destination in the 1950s and 60s
- Environmental challenges due to agricultural runoff
- Crucial habitat for migratory birds on the Pacific Flyway
- Focus of scientific study and restoration efforts
Ecological Challenges Facing Salton Sea
The Salton Sea, California’s largest lake, faces a myriad of ecological challenges that threaten its very existence and the health of its surrounding ecosystems. One of the most pressing issues is the high salinity levels, far exceeding those of the Pacific Ocean, making it inhospitable for most fish and bird species that once thrived there. This has led to massive die-offs, disrupting the food chain and affecting local wildlife populations.
Another significant challenge is water scarcity. The Salton Sea is primarily fed by agricultural runoff from nearby farms, which is decreasing due to more efficient irrigation techniques and the redirection of water to urban areas. This reduction in inflow causes the lake to shrink, increasing its salinity even further and exposing toxic dust from the lakebed. This dust, laden with agricultural chemicals and naturally occurring toxins like arsenic, poses severe air quality issues for surrounding communities, leading to health problems such as asthma and other respiratory issues.
Efforts to mitigate these challenges have been complex and multifaceted, involving water management strategies, habitat restoration, and air quality improvement projects. However, the scale of the problem and the need for coordinated action across multiple jurisdictions and stakeholders complicate these efforts. Without significant progress, the ecological balance of the Salton Sea and the health of its surrounding human and wildlife communities remain in jeopardy.
Strategies for Mitigating Ecological Challenges
Addressing the ecological challenges of the Salton Sea requires a comprehensive and multi-pronged approach. Restoration projects aimed at reducing salinity and controlling dust emissions are underway, with strategies including the creation of wetlands to serve as natural filters and dust control barriers. These efforts not only aim to improve water quality but also provide critical habitat for birds and other wildlife. Additionally, there is a push towards reducing agricultural runoff, promoting water conservation, and exploring alternative water sources to replenish the sea.
Future Prospects and Ongoing Research
The future of the Salton Sea hangs in a delicate balance, with ongoing research focused on finding sustainable solutions to its ecological crises. Scientists and policymakers are exploring innovative technologies and management practices that could potentially turn the tide, transforming the Salton Sea into a model for restoration and conservation in arid regions facing similar challenges. Success in these endeavors could provide valuable lessons for other areas grappling with the impacts of climate change, water scarcity, and environmental degradation.
| Challenge | Impact | Current Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| High Salinity | Decline in biodiversity | Creation of freshwater inflows |
| Water Scarcity | Shrinking lake size | Improved agricultural efficiency |
| Toxic Dust Exposure | Health issues in local communities | Wetlands for dust control |
| Habitat Loss | Decrease in bird populations | Habitat restoration projects |
| Climate Change | Exacerbation of existing issues | Research into adaptive management practices |
Recreational Activities at Salton Sea
The Salton Sea, a vast saline lake located in California’s Imperial and Coachella valleys, offers a variety of recreational activities despite the challenges it faces due to environmental issues. Once a thriving resort destination in the 1950s and 60s, the area around the Salton Sea still attracts visitors with its unique landscape and range of activities. Birdwatching is especially popular, as the lake is a vital stopover for several migratory bird species. The surrounding state recreation area provides opportunities for hiking, camping, and photography, enabling visitors to explore the stark beauty of this desert oasis.
Fishing was once a prominent activity at the Salton Sea, although it has declined in recent years due to fluctuating salinity levels and ecological changes. However, the lake’s shores offer serene spots for picnicking and sunset viewing, drawing visitors who seek tranquility away from the hustle and bustle of city life. The nearby towns, with their rich history and quirky art installations, provide an interesting contrast to the natural surroundings and are worth exploring.
For those interested in the environmental and conservation efforts, the Salton Sea area provides an educational experience. Various initiatives aim to restore habitats and manage the salinity and water levels of the lake, offering hope for its future. As such, the Salton Sea remains a place of intrigue and beauty, inviting the curious to discover its secrets and enjoy its quiet, desolate charm.
- Birdwatching for migratory species
- Hiking and camping in surrounding areas
- Photography of unique landscapes and wildlife
- Picnicking along the serene lake shores
- Exploring nearby towns and art installations
Future Prospects for Salton Sea
The Salton Sea, California’s largest lake, stands at a crossroads of environmental restoration and continued decline. The future of this saline lake is subject to ongoing debate, with efforts focusing on water quality improvement, habitat restoration, and local community support. As the Salton Sea recedes, it exposes toxic dust that poses health risks to nearby residents, making intervention critical. The State of California has committed to a series of projects aimed at shoring up the lake’s future, including the creation of wetlands to reduce dust emissions and improve habitat for wildlife. However, the success of these endeavors hinges on sustained funding and political will.
One of the most promising aspects of the Salton Sea’s future is the potential for geothermal energy development. The Salton Sea sits atop one of the most potent geothermal reservoirs in the United States, which, if fully developed, could provide a significant source of renewable energy. This energy potential, alongside initiatives to cultivate algae and tilapia, offers a glimpse into a sustainable economic model that could support the region’s revival. Despite these opportunities, the Salton Sea faces a precarious future, balancing on the edge of environmental disaster and economic rejuvenation.
Understanding the intricate balance between environmental restoration and economic development is crucial for the Salton Sea’s future. The efforts to save this ecological treasure are a testament to the complexity of managing natural resources in a changing climate. The path forward requires collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to the health of both the environment and the local communities.
| Project | Objective | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Wetlands Creation | Reduce Dust Emissions | Improved Air Quality |
| Geothermal Development | Renewable Energy Production | Increased Energy Supply |
| Habitat Restoration | Support Wildlife | Enhanced Biodiversity |
| Community Engagement | Local Support and Education | Enhanced Public Awareness |
| Economic Development | Create Sustainable Jobs | Economic Revival |
The Salton Sea’s future is a mosaic of challenges and opportunities. Efforts to mitigate its environmental issues while exploring avenues for sustainable development are crucial for the health and prosperity of the region. The journey towards rejuvenation is fraught with obstacles, but with persistent effort and innovative solutions, the Salton Sea can emerge as a model for managing natural resources in an era of ecological uncertainty.
As this discussion concludes, it’s clear that the Salton Sea’s fate is more than a regional concern; it’s a narrative on the global need for environmental stewardship and sustainable development. The path forward is complex, but with concerted effort and strategic planning, the Salton Sea can chart a course towards a brighter, more sustainable future.



Leave a Reply